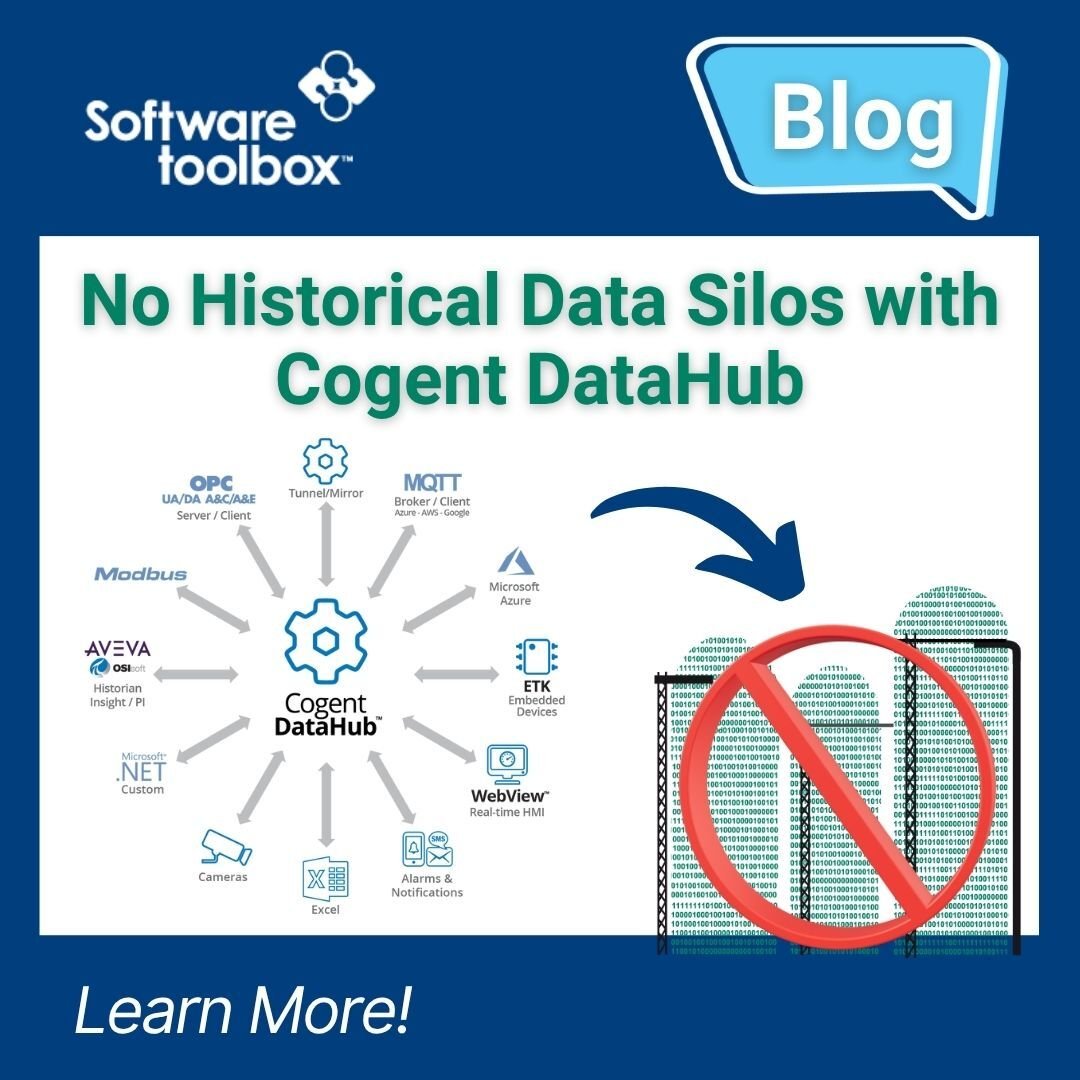
In the ever-growing digital landscape of manufacturing operations, single use solutions & applications may solve issues, but also create their own data silos. These silos present multiple challenges (limited visibility, slower decision-making, security blind spots) and lead to missed opportunities due to the complex management of varying solutions. For example, OPC HDA is a standard utilized for collecting and sharing historical data across industrial automation technology solutions. Based on the standards of OPC DA, integration challenges arise due to the dependency of COM and remote DCOM connections, creating incompatibility with newer solutions and technologies.
Today we'll explore how Cogent DataHub was used to solve many of these integration headaches and silos by providing a middleware platform for connectivity between a variety of protocols and technologies. With the latest major revision of Cogent DataHub V11, the ability to collect historical OPC HDA data is now possible with the addition of the OPC HDA Client capability.